2.10 Judicial system in SR
In the Slovak Republic we distinguish common courts and a special court which is the Constitutional Court of the Slovak Republic. The Common judicial system is executed by independent and neutral courts. The Judicial system in SR has two stages.
There are corresponding district courts for executing on the first stage. A regional court resolves as an appellate court. The Supreme Court of the Slovak Republic never acts as the highest body of judicial power on the first stage.
The Constitutional Court of SR is an independent judicial body of the constitutionality protection (article 124 of the Slovak Constitution). The Constitution of SR regulates the basic 2 Article 11, paragraph 4 (constitutional act no. 23/1991 Coll.) Page 27 of 74 position of the Constitutional Court and the position of the Constitutional Court judges. It makes decisions whether the regulations of the lower legal power are in compliance with the regulations of the higher legal power. Moreover, the Constitutional Court resolves even the questions of jurisdiction between the central bodies of the state administration if the law does not state that these questions are solved by another state body. The Constitutional Court makes decisions about different complaints, gives explanations of the Constitution or the constitutional law in disputable issues. More details about the organization of the Constitutional Court of SR are specified in particular legal regulations.
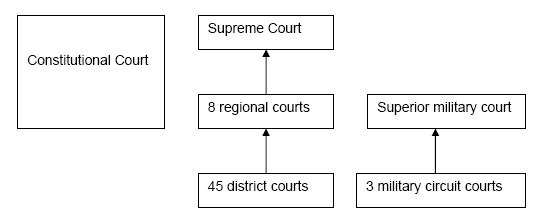
Source : Ministry of Justice SR
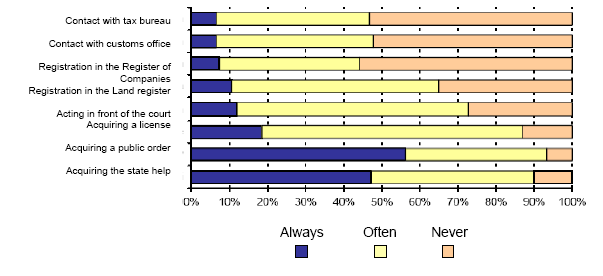
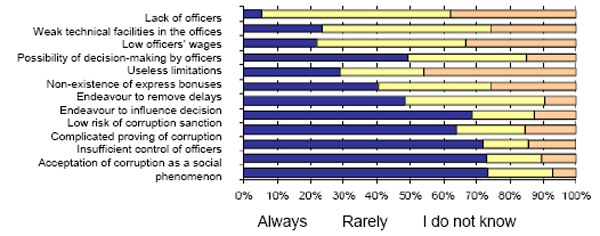
Source : Ministry of Justice SR
2.10.1 Law enforceability
The simplicity or complexity of the law enforceability is internationally measured by three indicators :In SR, the costs related to the law enforceability (of contracts) are 15 % of the debt comparing to 17.3 % which is a regional average and to 10.8 % which is the OECD countries average.
| Number of procedures | |||
| Duration (days) | |||
| Costs (% of debt) |
The table below shows the main indicators for the measuring of the law enforceability. These indicators include :
Slovakia thus belongs to the countries with the greatest number of procedures related to the law enforceability (27) and leads without precedence in the number of the days related to the law enforceability (565 days).